

The Graduate Center, CUNY, New York (GPA: 4.0)
The City College of New York, Feb 2014 (GPA: 3.9)
The City College of New York, Feb 2010 (GPA: 3.8)
Switching System, Analog Communications, Local Area Networks, Engineering Economics, Electrical Labs, Wireless Communications, Computer Communication Systems, Semiconductor Material Devices, Integrated Circuits, Fiber Optic Communications, Signal Processing, Stochastic Processes
Satellite Metreology, Statistics in Earth and Atmospheric Systems, Earth Systems, Fundamentals of Atmospheric Sciences, Dynamic Meterology, Dynamic Climate Change and Variability
The City College of New York, 2007
The City College of New York, Since 2007
The City College of New York, Since 2007
The City College of New York, Since 2007
The City College of New York, 2006
MATLAB, Python, C/C++, Fortran, C#, Shell Script, HTML/CSS
MySQL, PHP, PASCAL, Visual Basic, Java, GrADS, CUDA C, OpenACC
AutoCAD, OPNET, P-Spice, Lab View, MultiSim, Modelling Softwares
Microsoft Office (Word, Excel, Powerpoint, FrontPage & Access), Adobe Photoshop/Illustrator
LINUX (Fedora, Ubuntu, Red Hat, OpenSUSE, Kali), Mac OSX, DOS
Quick Learner, Leader/Team Player, Results & Knowledge driven
"Never, never, never give in." - Winston Churchill
Basketball, Hiking, Video Games
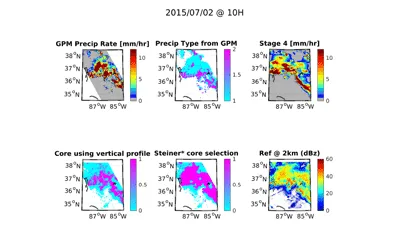
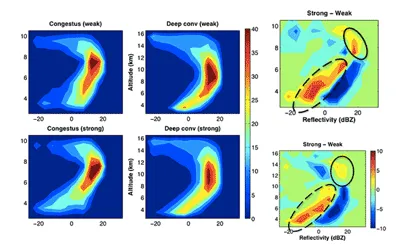
Extratropical cyclones (ETC) are the most common cause of extreme precipitation in mid-latitudes. Vertical motion within an ETC can be driven by isentropic lifting, upright convection and slantwise convection. These different mechanisms can deliver different rain rates, might respond differently to global warming, and the profile of condensational heating associated with these different pathways impact the storms differently. In this project we compare different metrics for identifying convection within the ETCs and calculate the relative contribution of convection to total ETC precipitation.
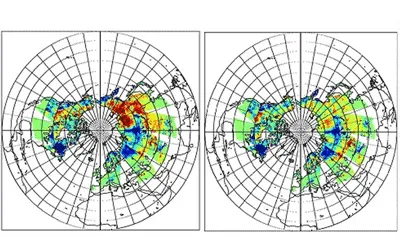
Snow is a key element of the water and energy cycles and the knowledge of spatio-temporal distribution of snow depth and snow water equivalent (SWE) is fundamental for hydrological and climatological applications. In this project, we develop a new operational algorithm applied to historical AMSR-E data using climatological data, electromagnetic modeling and artificial neural networks.
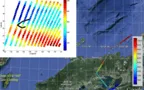
Convective vertical velocity is derived from time-delayed (1-2 min) IR measurements from MODIS and IIR. Convective vertical velocities are found to be clustered around 2-4 m/s but the distributions are positively skewed with long tails extending to larger values. Land convection during the 13:30 overpasses has higher vertical velocities than those during the 1:30 overpasses.
SSM/T2 satellites are first inter-calibrated within one another using relative calibration techniques such as zonal averages, natural target location and SNO. F14 was used as the base, because of the high availability of data and the overlap over all satellites.
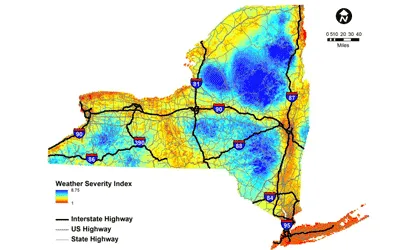
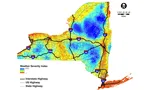
The objective of this project was to develop a plan for deploying a statewide RWIS to support both current NYSDOT operations and future MDSS applications. The recommended RWIS network shall provide and monitor timely road weather condition for decision making by road maintenance agencies.
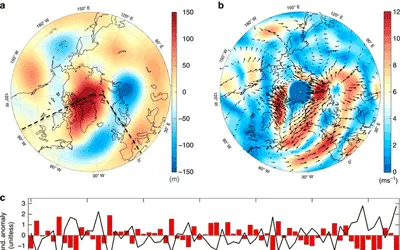
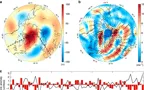
In this study, we compare MAR outputs with other model outputs from RACMO and satellite outputs. I was involved in the modification of running MAR with MERRA2 reanalysis data over Himalayas, Antarctica and Greenland.

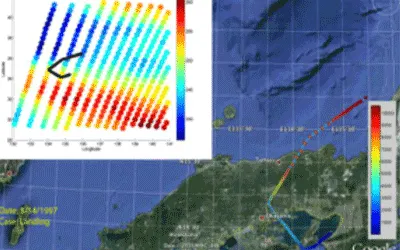
In this study, we try to predict the hurricane intensity by using the Moist Static Energy to estimate wind speeds, using Dr. Kerry Emanuel's method. We use data collected by NOAA hurricane hunters (reconnaissance data).
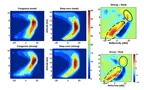

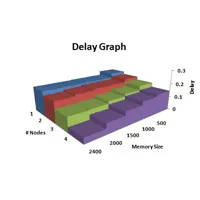
Designed OPNET algorithm to improve quality of video transfer from one node to another via ad hoc Network, by using buffered smart nodes.
Created system-in-the-loop setup with multiple machines and real-life data packets to analyze bit rate, packet loss ratios and SNR.
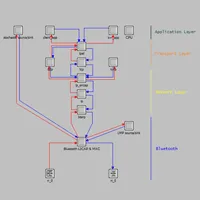
Created packet switched network in OPNET using dynamic routing protocol for specified network design.
Simulated VOIP scenario over ad hoc Network. Built and improved performances of video transfer over a Bluetooth Mobile ad hoc Network.
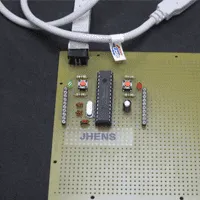
Designed USB interface device capable of controlling actuators.
Scripted software patch for use with Arduino Programming Language to program PIC. Team leader of 5 holding weekly status meetings to monitor progress and resolve project obstacles.

Designed OPNET algorithm to improve quality of video transfer from one node to another via ad hoc Network, by using buffered smart nodes.
Created system-in-the-loop setup with multiple machines and real-life data packets to analyze bit rate, packet loss ratios and SNR.

Created packet switched network in OPNET using dynamic routing protocol for specified network design.
Simulated VOIP scenario over ad hoc Network. Built and improved performances of video transfer over a Bluetooth Mobile ad hoc Network.

Designed USB interface device capable of controlling actuators.
Scripted software patch for use with Arduino Programming Language to program PIC. Team leader of 5 holding weekly status meetings to monitor progress and resolve project obstacles.
J. Jeyaratnam, J. F. Booth, C. M. Naud, Z. J. Luo and C. R. Homeyer: Geophysical Research Letters, 47, e2019GL086620
C. M. Naud, J. Jeyaratnam, J. F. Booth, M. Zhao and A. Gettelman: J. Climate, 33, 95-113
C. M. Naud, J.F. Booth, J. Jeyaratnam, et al.: J. Climate, 32, 6685-6701
J. F. Booth, C. M. Naud and J. Jeyaratnam: Geophysical Research Letters
L. Smith, K. Yang, L. H. Pitcher, et al., M. Tedesco, J. Jeyaratnam, et al.: PNAS 114, no. 50
M. Tedesco, and J. Jeyaratnam: Remote Sensing (MDPI), 8, 1037
M. Tedesco, T. Mote, J. Jeyaratnam, et al.: Nature Communications, 7, 11723
M. Tedesco, S. Doherty, X. Fettweis, P. Alexander, J. Jeyaratnam, and J. Stroeve: The Cryosphere, 10, 477-496
M. Tedesco, J. Jeyaratnam, and R. Kelly: NASA LANCE AMSR2 at the GHRC DAAC
M. Tedesco, M. Sartori, and J. Jeyaratnam: IEEE IGARSS, pp. 4037-4040
Z. J. Luo, J. Jeyaratnam, S. Iwasaki, H. Takahashi and R. Anderson: Geophys. Res. Letts., 41